What is Screen Space Ambient Occlusion (SSAO)?
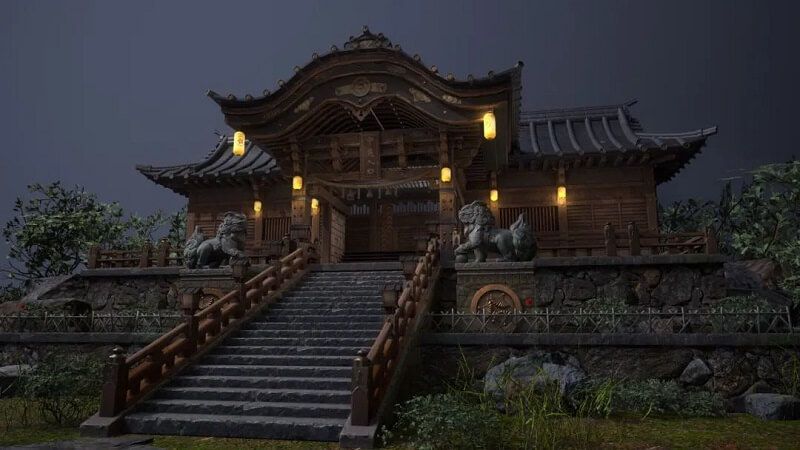
A game scene may look sharp, yet something still feels flat. Walls touch the floor, objects meet the table, but the contact areas look too clean and unreal. This is where Screen Space Ambient Occlusion, or SSAO, makes a big difference. SSAO adds soft, dark areas in corners and tight spaces to show where light has less reach, and helps scenes feel deeper and more natural.
In this guide, you’ll learn what Screen Space Ambient Occlusion is, how SSAO works, and its limitations compared to other ambient occlusion techniques. We’ll also explain when and where to use SSAO in games, real-time rendering, and 3D visualization.
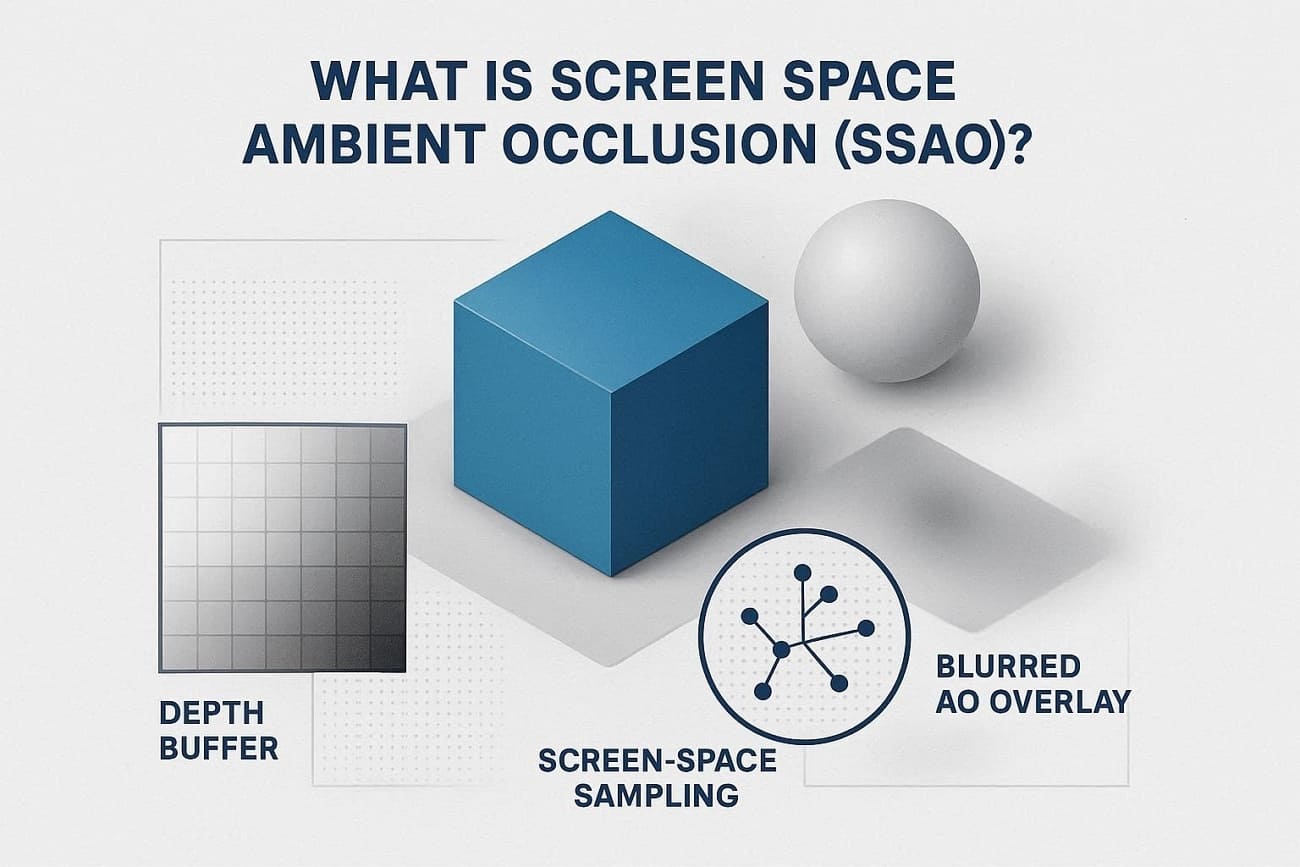
Part 1. What is Screen Space Ambient Occlusion?
Screen Space Ambient Occlusion, or SSAO, is a graphics method that makes corners, creases, and contact areas look darker. To further know what SSAO is, know that it shows where light reaches less, so tight spaces appear shaded. Additionally, SSAO works only with what is visible on the screen, not the full 3D scene.
This makes it fast for real-time use, since performance depends mainly on screen resolution rather than scene complexity or polygon count, and overall cost. As a result, it improves depth and realism, making walls, floors, and objects feel more grounded and natural without heavy processing or extra geometry.
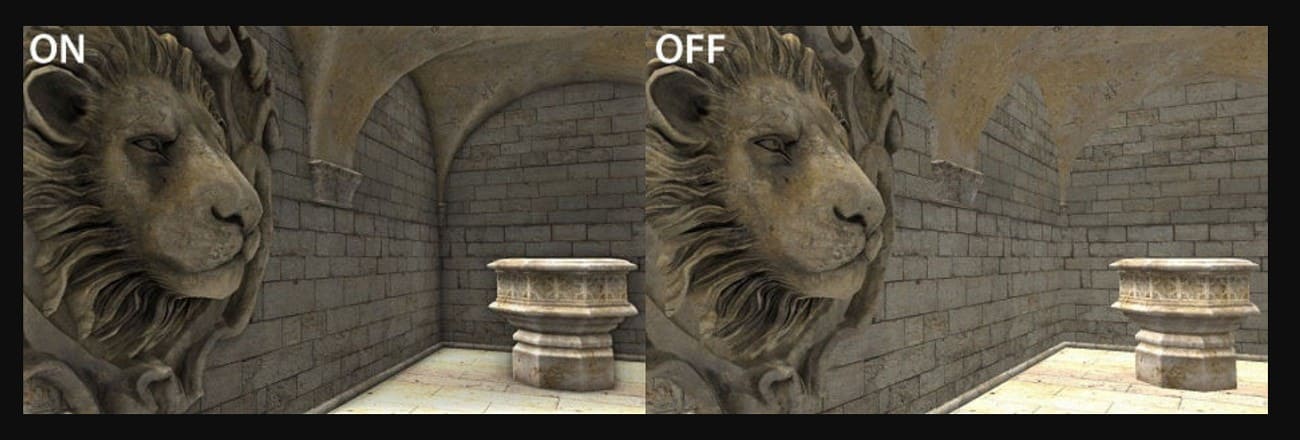

Part 2. How Does SSAO Work?
SSAO works as a post-processing step that reads depth from the rendered image and darkens pixels where light is blocked, especially in corners and contact areas. So, now that you are clear on the SSAO meaning, let’s see in detail how SSAO works:
1. Use Depth (And Normal) Buffers
When the scene renders, the engine has a depth buffer "distance from the camera per pixel" and often a normal buffer "surface direction per pixel." SSAO runs as a full-screen pass using these buffers instead of checking the whole 3D scene.
2. Sample Nearby Points to Estimate Occlusion
For each pixel, SSAO looks at nearby positions on screen, and if nearby geometry is closer, it blocks light. More blocked points make the pixel darker and show creases, corners, and contact areas.
3. Blur and Composite the Occlusion
Raw occlusion can look noisy, so a depth-aware blur smooths it while keeping edges. The result is added to the image to darken corners and give a sense of depth. However, it only uses what’s visible on screen, so it can’t detect hidden or off-screen objects.
Part 3. SSAO Performance Considerations and Limitations
While you know what SSAO in graphics is, it's essential that you adhere to the listed considerations and limitations for this graphics method. Upon doing so, you will be able to achieve realistic ambient shading effects in your 3D scenes without compromising performance.
Performance Considerations
1. Cost Scales: Cost depends mostly on screen resolution and sample count, not scene polygons. 4K with high refresh rates and many samples is heavy for GPUs.
2. Sample Count and Radius: More samples and a larger radius improve quality but increase GPU workload. Engines offer low, medium, high, or sliders for the sample count radius.
3. Extra Buffers: SSAO needs depth and normal textures, which add rendering passes and overhead. Ambient Occlusion and blur passes are full-screen operations that increase fill rate.
4. Downsampling: Compute SSAO at half or quarter resolution, then upsample to save time. Reduce samples, limit radius, or adapt the quality to the camera distance.
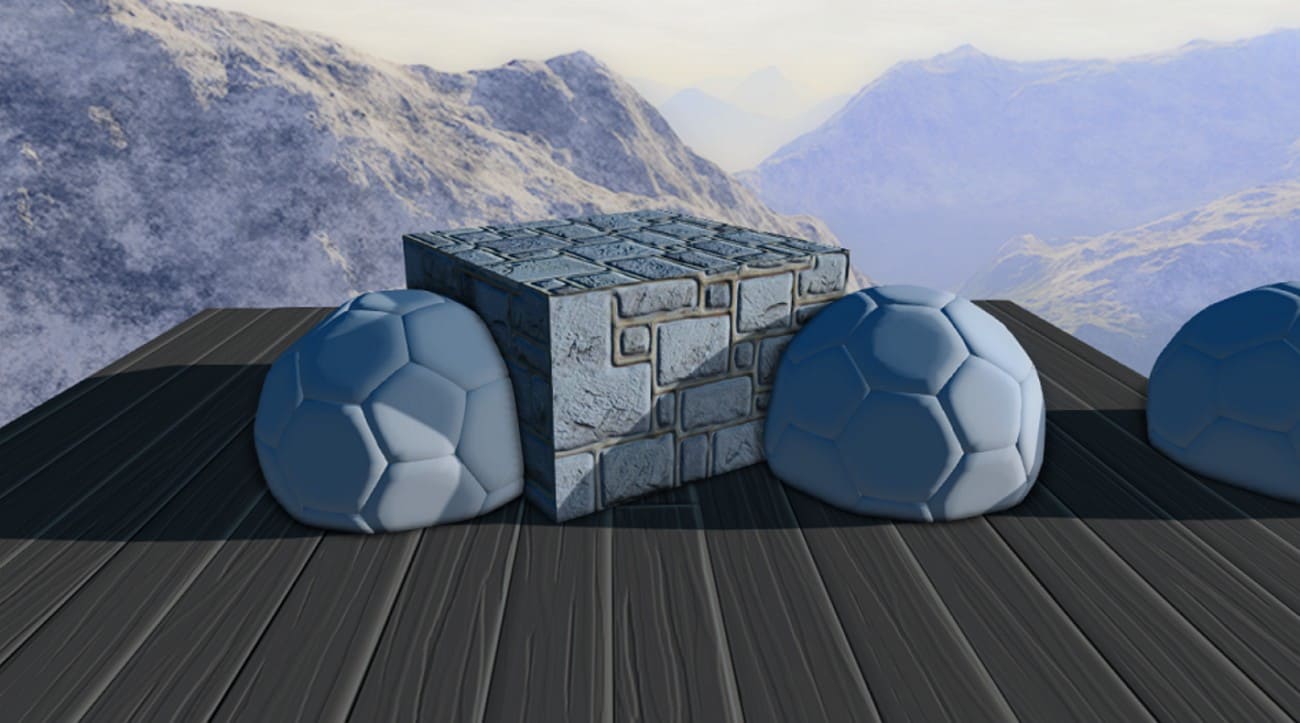
Visual Limitations
- SSAO only sees what is in the current frame depth and normal buffers.
- Occlusion changes with camera angle or FOV, causing popping or inconsistency.
- Low sample counts create noisy speckled AO requiring blur to fix.
- SSAO approximates ambient occlusion less accurately than ray-traced AO.
Cloud-Based Rendering for Better SSAO Performance
In real-time previews like games, SSAO must run fast, so quality and resolution are limited. For cinematic sequences in engines like Unreal Engine, teams often use higher resolution, stronger AO, and more samples, which can be too heavy for local machines.
In these cases, you can send the project to a dedicated render farm that is integrated with Unreal Engine, such as Fox Renderfarm. This lets you keep high-quality AO and lighting while the heavy rendering runs across many remote computers rather than your own GPU.

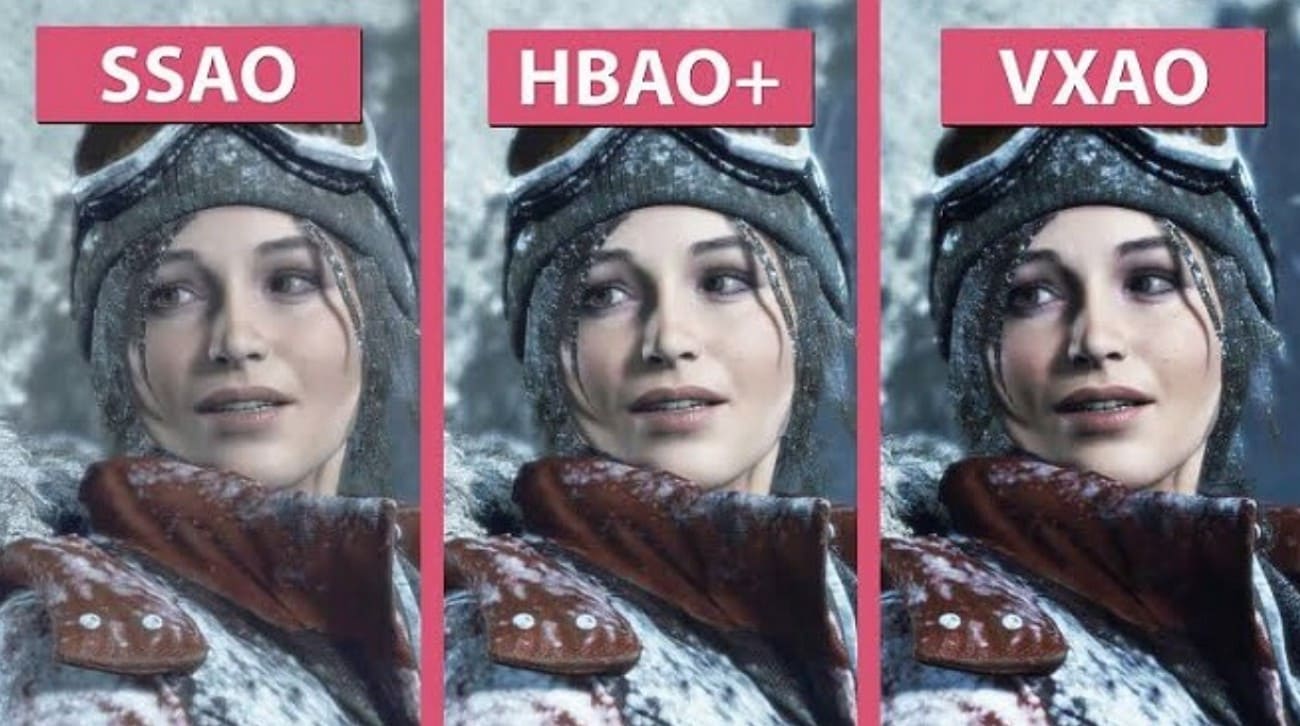
Part 4. SSAO vs HBAO vs HDAO
Know that SSAO, HBAO, and HDAO differ in quality, performance, and occlusion accuracy. Therefore, as you know what Screen Space Ambient Occlusion is, compare it with HBAO and HDAO, and determine the difference:

|
Aspect |
SSAO (Screen Space AO) |
HBAO (Horizon-Based AO) |
HDAO (High-Definition AO) |
|
Who Made It |
General technique, first popularized by Crytek |
Developed by Nvidia |
Developed by AMD |
|
Basic Idea |
Samples nearby depth in screen space to darken creases and corners |
Uses horizon-based sampling in screen space to better estimate visible occlusion |
Screen space AO method optimized for higher detail and contrast |
|
Visual Quality |
Simplest and fastest; may appear noisy or halo-like |
Cleaner and more stable local occlusion than basic SSAO |
Higher contrast and sharper occlusion, sometimes visually heavy |
|
Performance Cost |
Lowest cost; suitable for low to mid-range hardware |
Higher than SSAO, with balanced quality and performance |
Can be demanding depending on implementation and settings |
|
Typical Usage |
Widely available across engines and games |
Common in engines and games, often with enhanced variants like HBAO+ |
Historically associated with AMD GPUs, it is less common in modern engines |
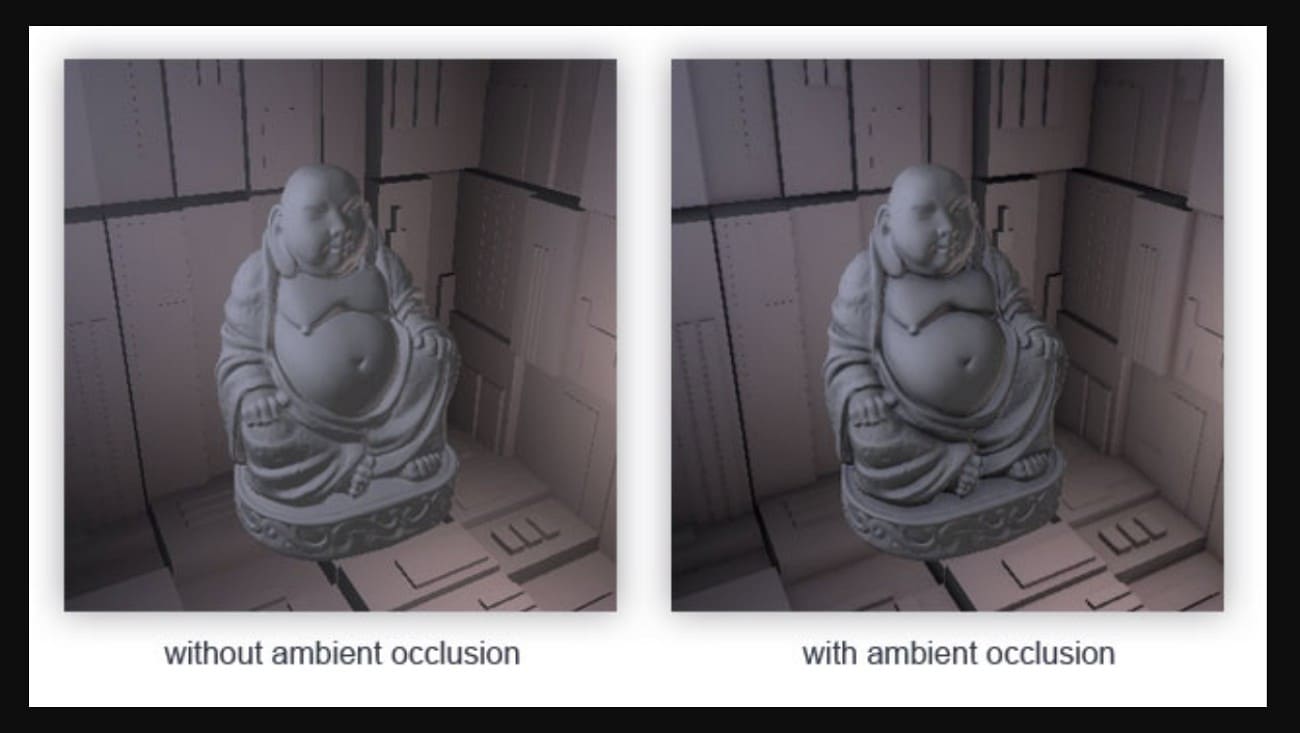
Part 5. Why SSAO Matters in 3D Graphics?
If you ask what SSAO is in graphics, know that it is essential because it adds soft shadows and depth to a 3D scene. Thus, this makes objects feel solid and real without heavy ray-traced lighting. It darkens corners, creases, and contact areas where light cannot reach, preventing flat-looking scenes. These shadows separate objects, improve readability, and give a natural, grounded look.

With all these aspects, an artist can adjust SSAO strength, radius, and bias for subtle or stylized effects, and use it as a mask for dirt, wear, or cavity shading. Above all, it operates in screen space using depth and, sometimes, normals, so its cost depends on resolution, not scene complexity.
Part 6. Where is SSAO Used?
After you know the hype of SSAO modes in graphics, you might want to know where it can be used and how. To that end, review the 3 listed use cases and see how each enhances 3D visuals and realism.
1. Games and Real-Time Engines
SSAO has become popular in games and real-time engines such as Unreal Engine and Unity to darken creases, corners, and contact points between objects. This renders scenes less flat and more natural and is very widespread in first-person and third-person games, racing games, and open-world scenes. These games feature rich detail, but lighting must stay fast and real-time, so SSAO adds depth and contact shading with minimal performance cost.

2. Interactive Visualization and VR
In interactive visualization and VR, SSAO is used in real-time architectural tours, product viewers, and technical visuals. It helps models look solid and physical while keeping fast frame rates. SSAO also appears in many VR apps because it improves depth perception at a much lower cost than ray-traced ambient occlusion.

3. 3D Content Tools and Viewers
SSAO in 3D content tools and viewers is built into many real-time renderers and preview modes. It appears in tools like Blender Eevee and engine viewports as an on or off effect. Additionally, artists use it in model viewers and WebGL demos to show assets with better shading. This gives nicer previews without the need to bake ambient occlusion maps.
Part 7. FAQs about SSAO
1. Is SSAO better than HBAO?
SSAO is faster, but HBAO often gives cleaner and more stable shadow detail in many cases. However, SSAO uses less power, so it suits low and mid-range systems for real-time.
2. Does SSAO affect CPU or GPU?
Screen Space Ambient Occlusion mainly affects the GPU, since it runs as a screen effect in most cases. Meanwhile, CPU load stays low, but a higher resolution can raise GPU workload in heavy scenes.
>> Related: CPU vs GPU: Which One is Best for Your Project?
3. Does SSAO replace ray-traced AO?
No, SSAO cannot replace ray-traced AO for full and accurate light cover in all. However, SSAO is a fast option, so it fits real-time use on many systems.
Conclusion
To sum up, this ultimate guide has explained what Screen Space Ambient Occlusion means and how it is used. Additionally, it covered limits, performance balance, and common use cases in games, VR, and visualization.
For high-resolution or cinematic workflows that push beyond local hardware limits, using a cloud render farm that supports Unreal Engine (such as Fox Renderfarm) can be a practical option to offload heavy rendering tasks and reduce local rendering time.





