Learn Parallax Mapping: Add Depth and Realism to Your 3D Scenes
Most 3D artists and game developers have difficulties in making flat surfaces appear real without taking an extra polygon. Walls, floors, and objects are also seen to be flat, even in quality scenes. In this case, parallax mapping is the solution, providing textures with an appearance of depth and detail without additional geometry.
Artists are able to make complex-looking scenes at a fast pace and still perform well. Thus, if you are keen to know about this technique, go through this guide to know what it is, how it works, and how it is applied.
Part 1. What is Parallax Mapping?
Parallax mapping is a graphics technique that makes flat surfaces appear to have real depth, such as bumps or holes, without adding extra geometry. It uses a height map, a black-and-white image where bright areas are high and dark areas are low. Hence, the shader moves the texture slightly based on the viewer’s position and the height map.

This causes sections of the surface to seem to move at varying degrees when looking at it at various angles. Therefore, the outcome is a flat texture appearing three-dimensional that provides walls, floors, and objects with greater realistic detail without additional polygons.
Part 2. How Does Parallax Mapping Work?
After understanding the basics, you might want to know how this technique works in detail. Hence, here’s how a parallax map creates depth and realism in 3D scenes.
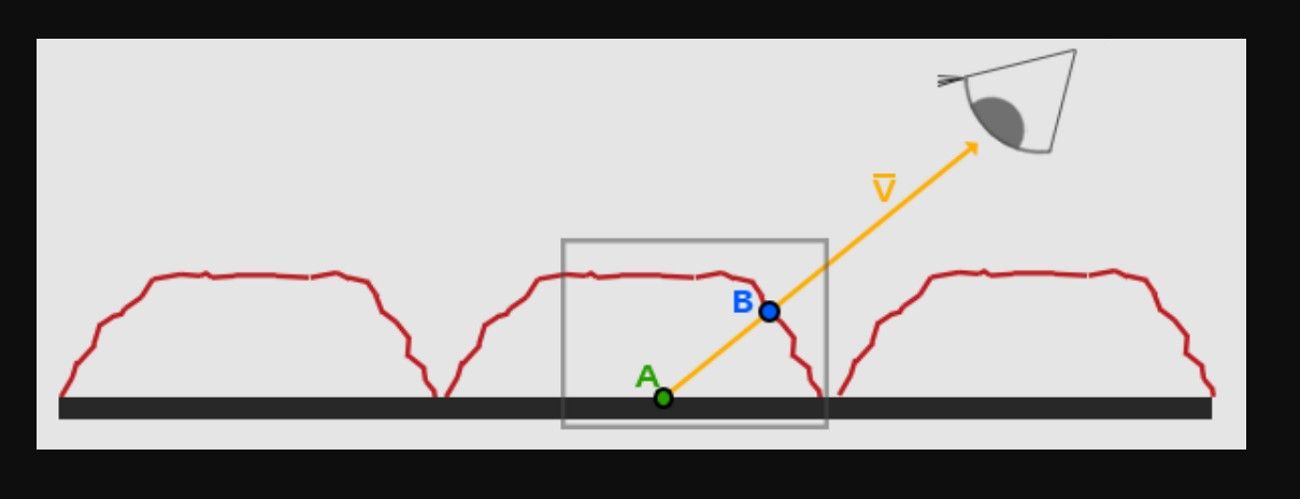
1. Core Inputs
- Height Map: A black-and-white texture where bright parts are high and dark parts are low on the surface.
- View Direction: A line from the surface point to the camera, usually aligned with the surface’s UV layout.
2. Basic Offset Calculation
For each pixel, the shader reads the height map at the current UV position to get the height, then uses the view direction to shift the UVs.
The offset is roughly: offset ≈ viewDir.xy / viewDir.z × height × scale
At shallow angles, the shift is greater, making depth appear stronger inside views.
3. Sampling with Displaced UVs
After finding new UVs, the shader reads the color and normal maps there, so high areas move more than low ones. Thus, this makes the flat surface look 3D as the camera moves.
4. Advanced Variants
Steep parallax or parallax occlusion mapping uses multiple steps along the height to find surface intersection. This improves depth accuracy on steep angles, but needs more GPU work.
Part 3. Real-Life Applications of Parallax Mapping
The parallax mapping technique is used when you want surfaces to look 3D without adding many polygons. So, to know where one can apply this technique and get parallax textures, review some of its applications given below:
How is Parallax Mapping Used in Video Games for Environment Textures?
It gives depth to walls, floors, rocks, bricks, tiles, and ground so as to appear cracked or stratified, and the mesh remains basic. This allows first and third-person games to appear more realistic, particularly at side angles with no high-performance cost.

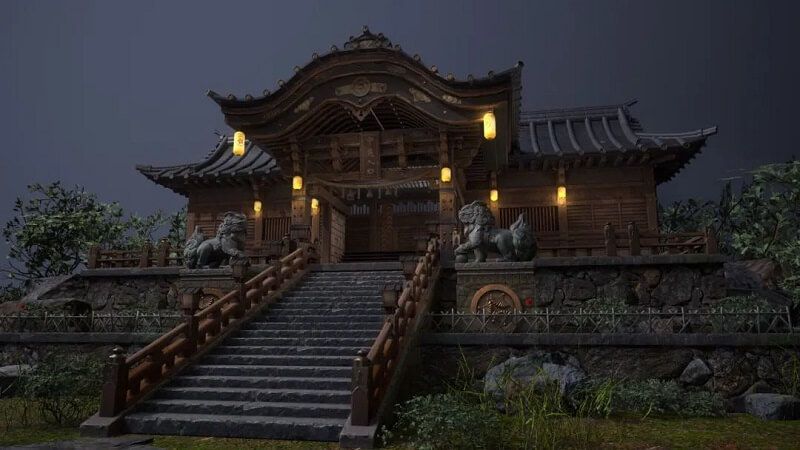
How Does Parallax Mapping Enhance Architectural Visualization?
Architects use it on brick, stone, wood panels, and decor to show depth without model detail. This keeps scenes light for real-time walkthroughs while still making walls, floors, and ceilings look detailed.
How Is Parallax Mapping Applied in VR and AR Experiences?
In VR and AR, fast speed is important, so parallax mapping adds surface depth without heavy meshes. The view-based texture shift makes depth feel stronger than basic normal maps.
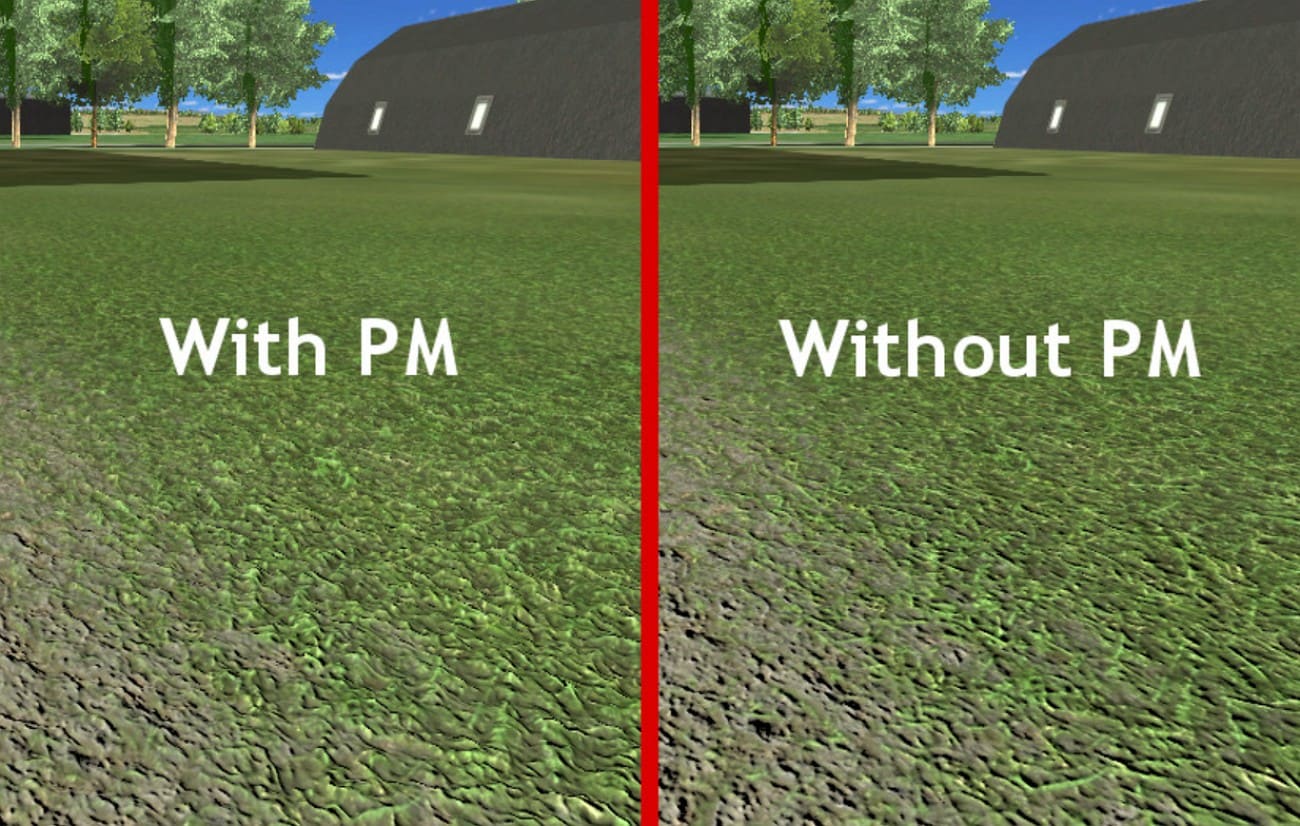
How Does Parallax Mapping Improve Product Visualization?
It fakes stitching, embossing, and patterns on simple models like shoes, bags, or furniture. This gives a rich look in real-time previews without complex geometry.
How is Parallax Mapping Used in Real-Time Cinematic and Cut Scene Content?
In cinematics, it adds depth to streets, walls, and sci-fi panels in real-time scenes and trailers. Additionally, it gives better depth than normal maps and costs less than full displacement.
Part 4. How to Create Parallax Mapping in Unreal Engine / UE5
Parallax mapping in Unreal Engine 5 uses a height map with the Parallax Occlusion Mapping material function. Thus, this adds fake depth to flat surfaces before the final render. For those who want to know how to use the parallax shader in Unreal Engine / UE5, adhere to its detailed guide for clarity:
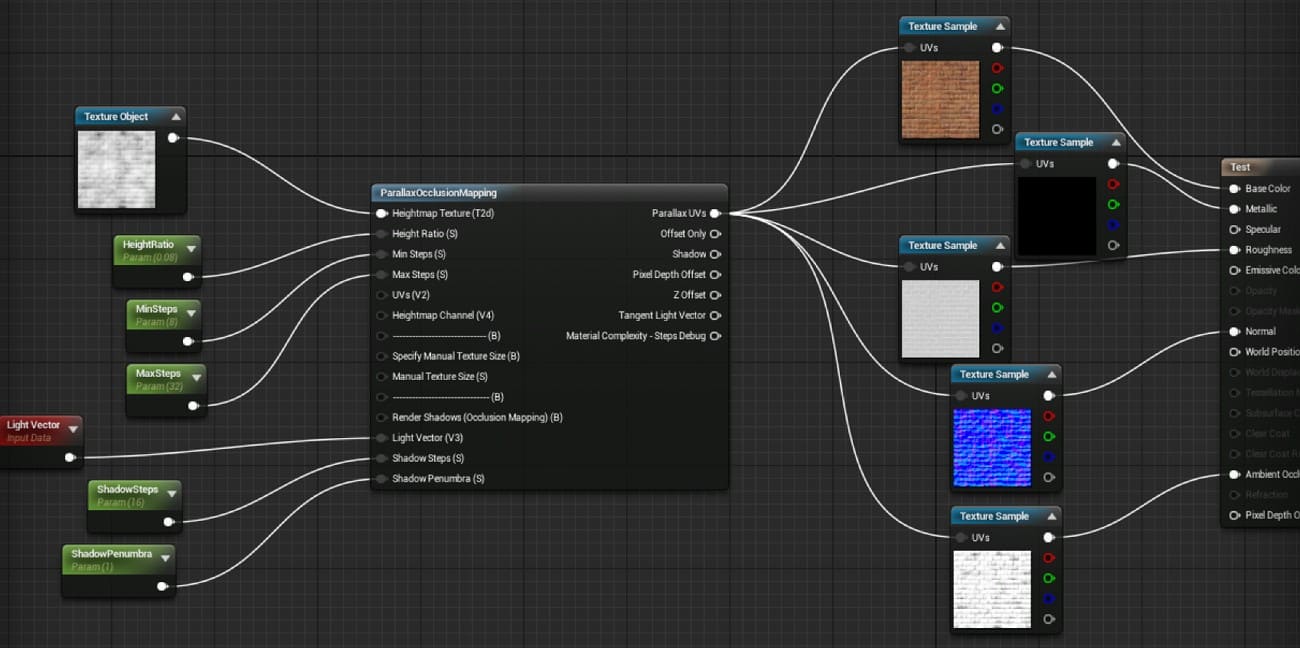
1. Prepare Assets and Materials
Import base color, height or displacement, normal, and roughness or AO textures for the surface.
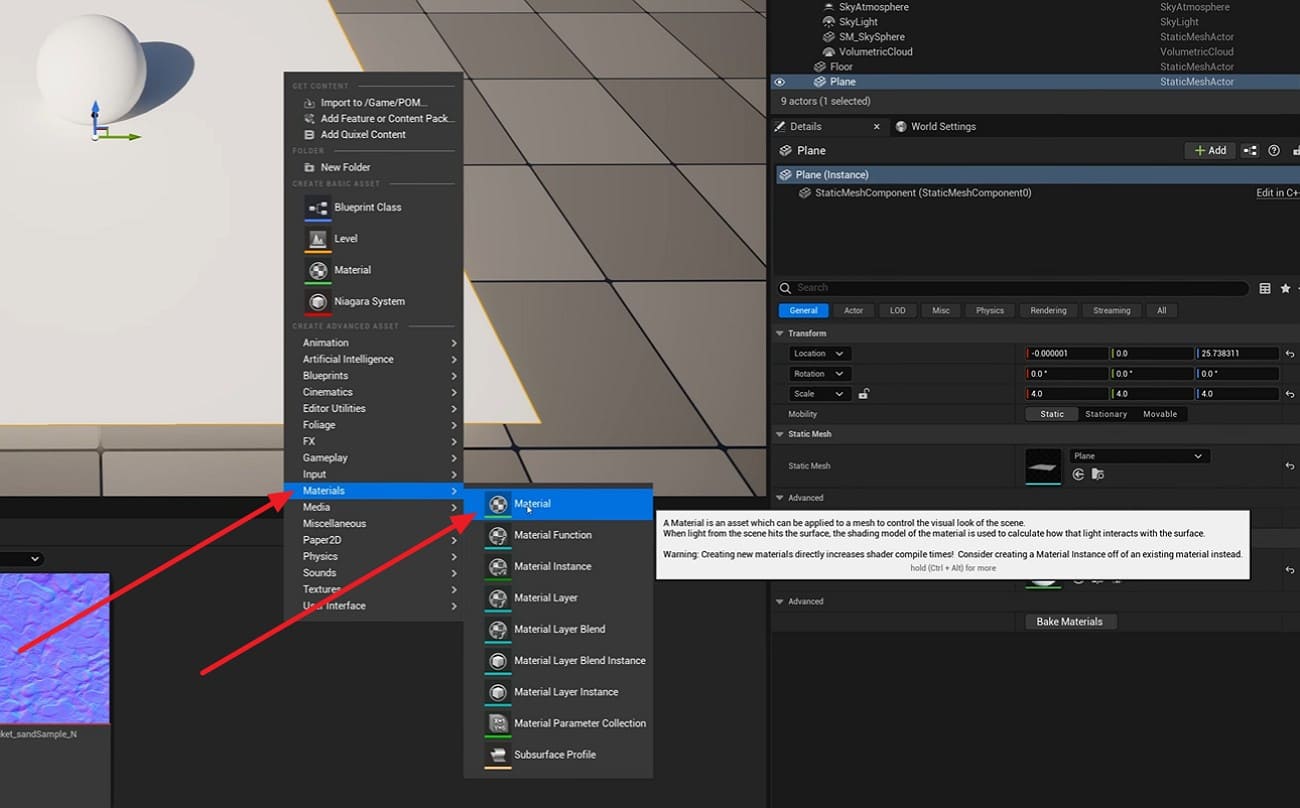
After that, create a new Material by right-clicking on the tool, and set Material Domain to Surface and Shading Model to Default Lit for most surfaces.
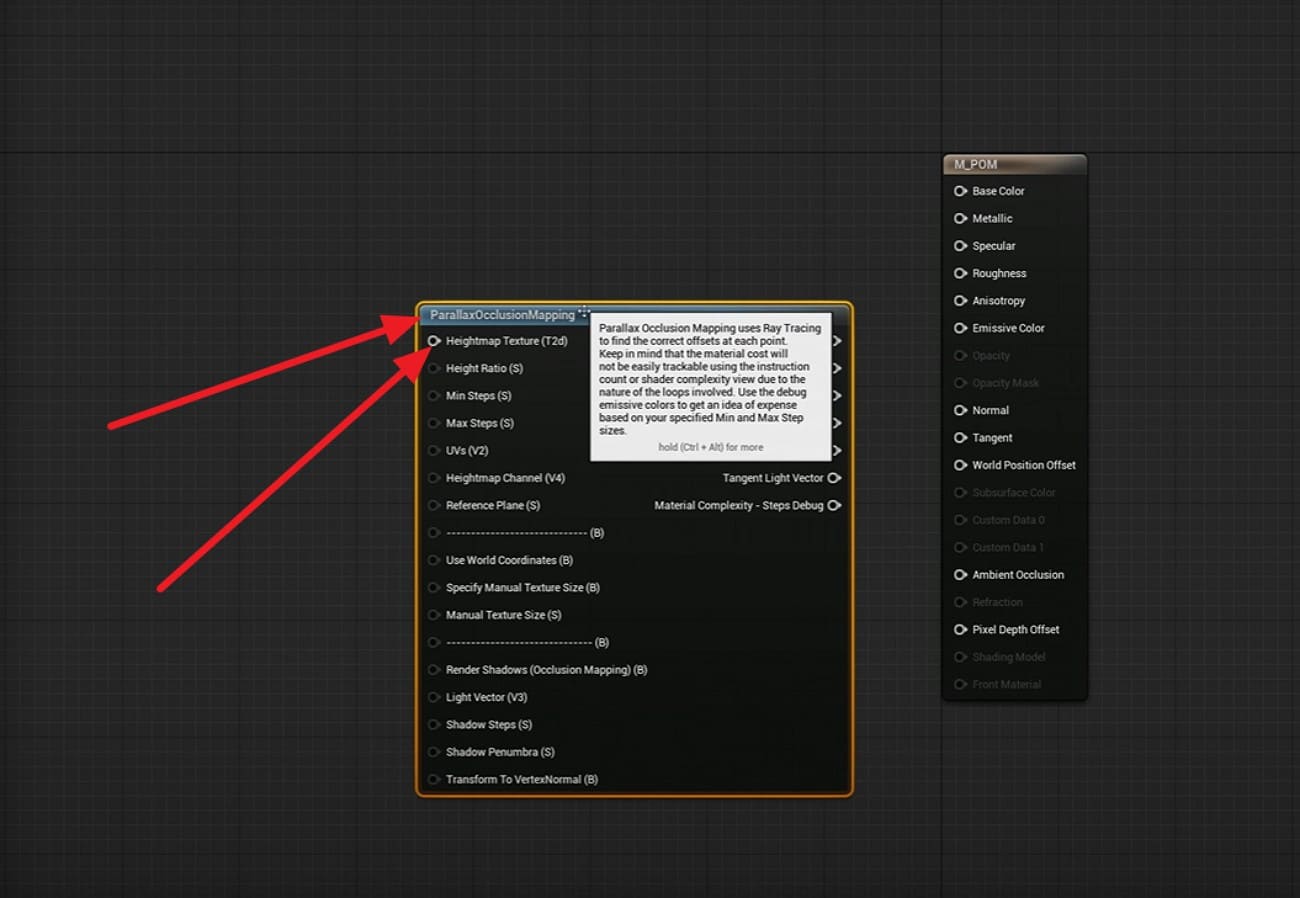
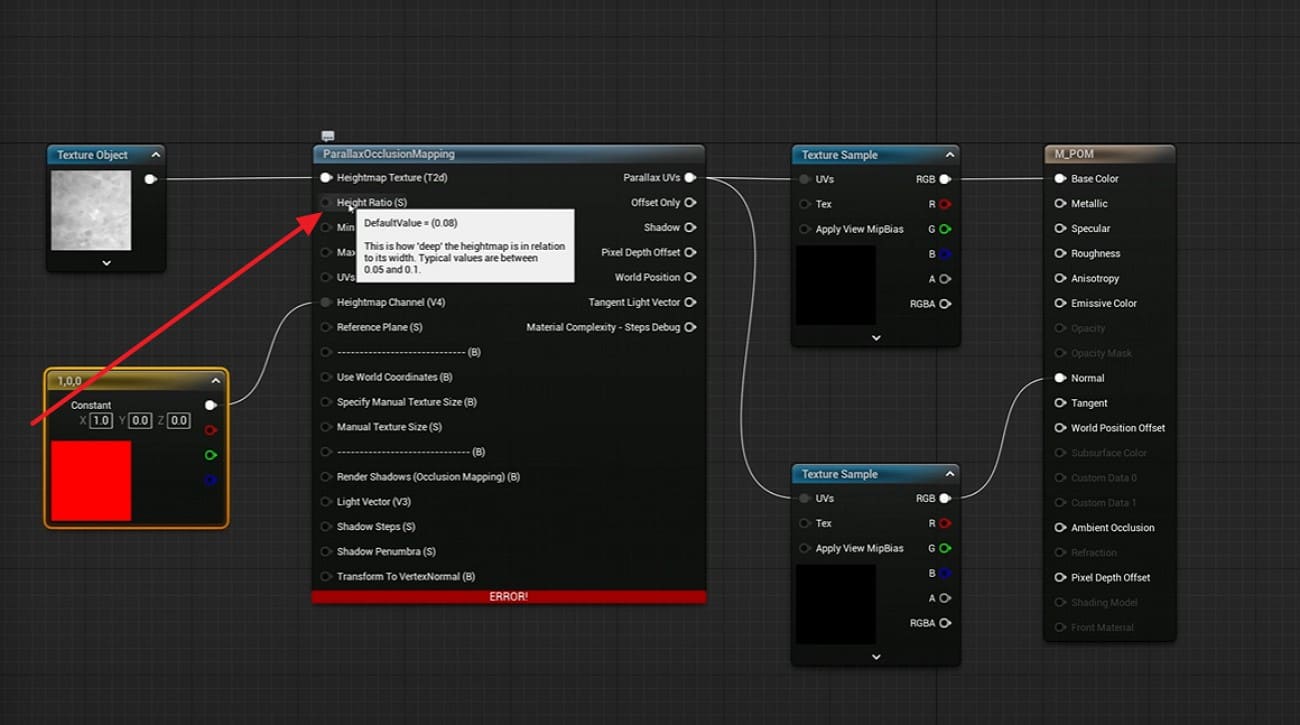
2. Add Parallax Occlusion Mapping
In the Material Editor, add the Parallax Occlusion Mapping function node as you right-click on the tool. After that, change the height texture sample to a Texture Object. Later, connect it to the Height Map input on the function.
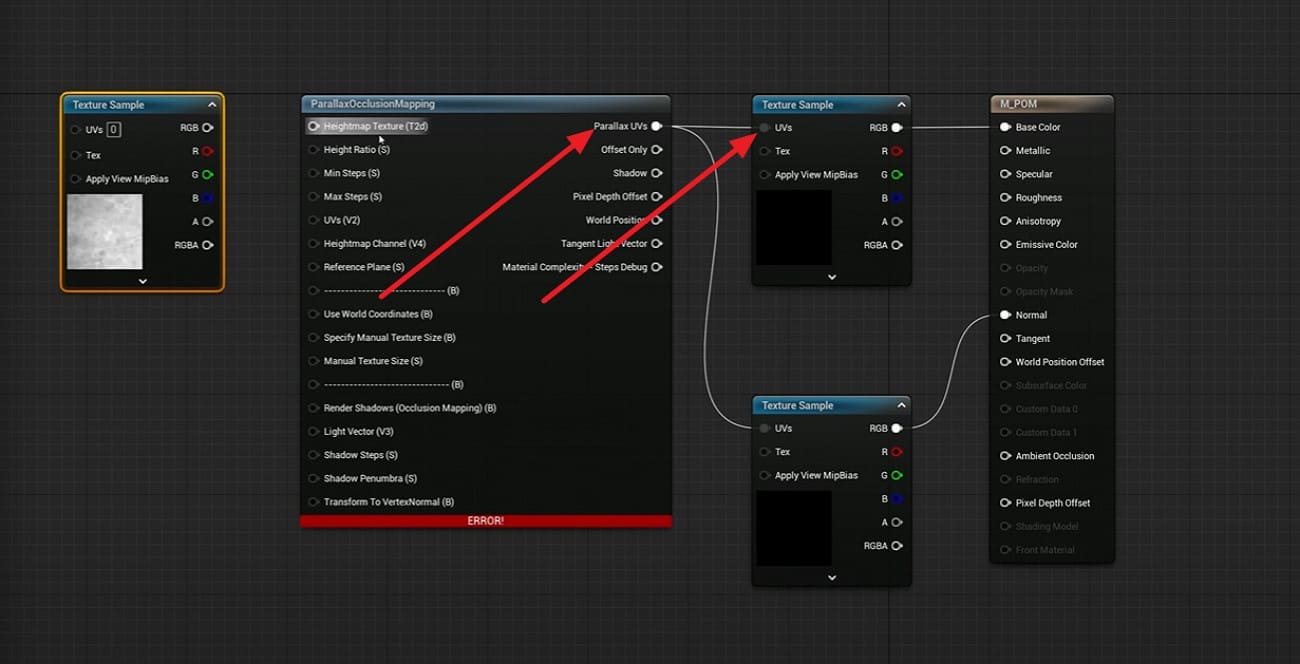
3. Connect UVs and Textures
Add a TextureCoordinate node or use custom UVs, and connect it to the UVs input on the POM node. Use the POM output UVs for base color, normal, and other textures, and then connect those to the main material inputs.
4. Tune Depth and Quality
Now, add scalar parameters for Height Ratio and Min or Max Steps, which allow easy depth and quality control. Use low step values for games and higher values for close views. Know that too much depth can cause shimmer and slow speed.
5. Apply, Test, and Render
Apply the material to walls or floors, move the camera at side angles, and adjust values until depth looks right. For the final 4K or 8K scenes, heavy materials and high resolution can stress hardware, leading to long render times.
In high-end cases, you can export your Unreal Engine sequence and use a render farm like Fox Renderfarm. It supports Unreal Engine cloud render, so you can upload your project and let remote CPU and GPU systems handle heavy renders instead of your own PC.

Part 5. Parallax Mapping vs Normal Mapping vs Displacement Mapping
While learning about the parallax algorithm, it is important to understand what the difference between parallax mapping, normal mapping, and displacement mapping is. Each technique affects surface depth, visual realism, and performance in different ways within 3D rendering.
|
Aspect |
Normal Mapping |
Parallax Mapping |
Displacement Mapping |
|
What It Does |
Modifies surface normals to simulate small bumps in lighting only |
Shifts texture UVs per pixel using a height map and view direction to simulate surface depth |
Physically alters geometry by moving vertices or micropolygons using a displacement map |
|
Geometry Changed? |
No – mesh remains flat |
No – mesh remains flat |
Yes – actual geometry and silhouette are modified |
|
Depth Illusion Strength |
Good for fine surface detail, but breaks at steep viewing angles |
Stronger depth illusion than normal mapping, but still fails at extreme grazing angles |
True physical depth that remains accurate from all viewing angles |
|
Performance Cost |
Lowest – minimal GPU cost, ideal for real-time |
Medium – additional per-pixel calculations and texture sampling |
Highest – requires subdivision or tessellation and significantly more memory and processing |
|
Typical Use Cases |
Games and real-time assets for subtle detail like scratches, fabric weave, and pores |
Surfaces like bricks, tiles, floors, and walls, where depth is needed without extra geometry |
Film, VFX, and high-end ArchViz for close-ups where real relief and silhouettes are critical |
Part 6. FAQs about Parallax Mapping
1. What is parallax in simple terms?
Parallax means objects seem to move at different speeds when you change your view. Near parts shift more than far parts, which makes depth feel more real.
2. Is parallax occlusion mapping expensive?
Yes, it costs more GPU power than basic parallax or normal maps. It uses many texture reads per pixel, so the frame rate may drop on weak hardware.
3. What are the best software tools for implementing parallax mapping?
Popular tools include Unreal Engine, Unity, Blender, and Substance Designer for texture work. Game engines and shader tools help set height maps and depth scale values.
Conclusion
To sum up, this guide has explained what parallax mapping is and how it works to add depth to flat surfaces. It also showed where this method fits best, such as games, visuals, and real-time scenes. However, for large or high-quality projects, a render farm like Fox Renderfarm is suggested as it can help handle heavy render work and save local system time.





