What Is Global Illumination in 3D Rendering and How It Works
As 3D graphics become more realistic, many beginners wonder why some renders look flat or dull compared to real life. That's why global illumination becomes important. It makes scenes appear natural by revealing the reflection of light on objects and surfaces.
Global illumination adds depth and life by simulating indirect light in a scene. This effect makes shadows softer and colors more accurate without extra effort. Even simple 3D models can feel more believable when global illumination is applied. Thus, in this article, we explain what is global illumination, how it works, along with a few usage tips.

Part 1. What Is Global Illumination in 3D Rendering?
Global illumination, or GI, is a form of lighting effect used to make 3D scenes look real. Instead of calculating only direct light from a single source, global illumination also computes how light bounces off walls, floors, and other surfaces. This light, reflecting and bouncing, illuminates darker spaces and gives natural color shades.
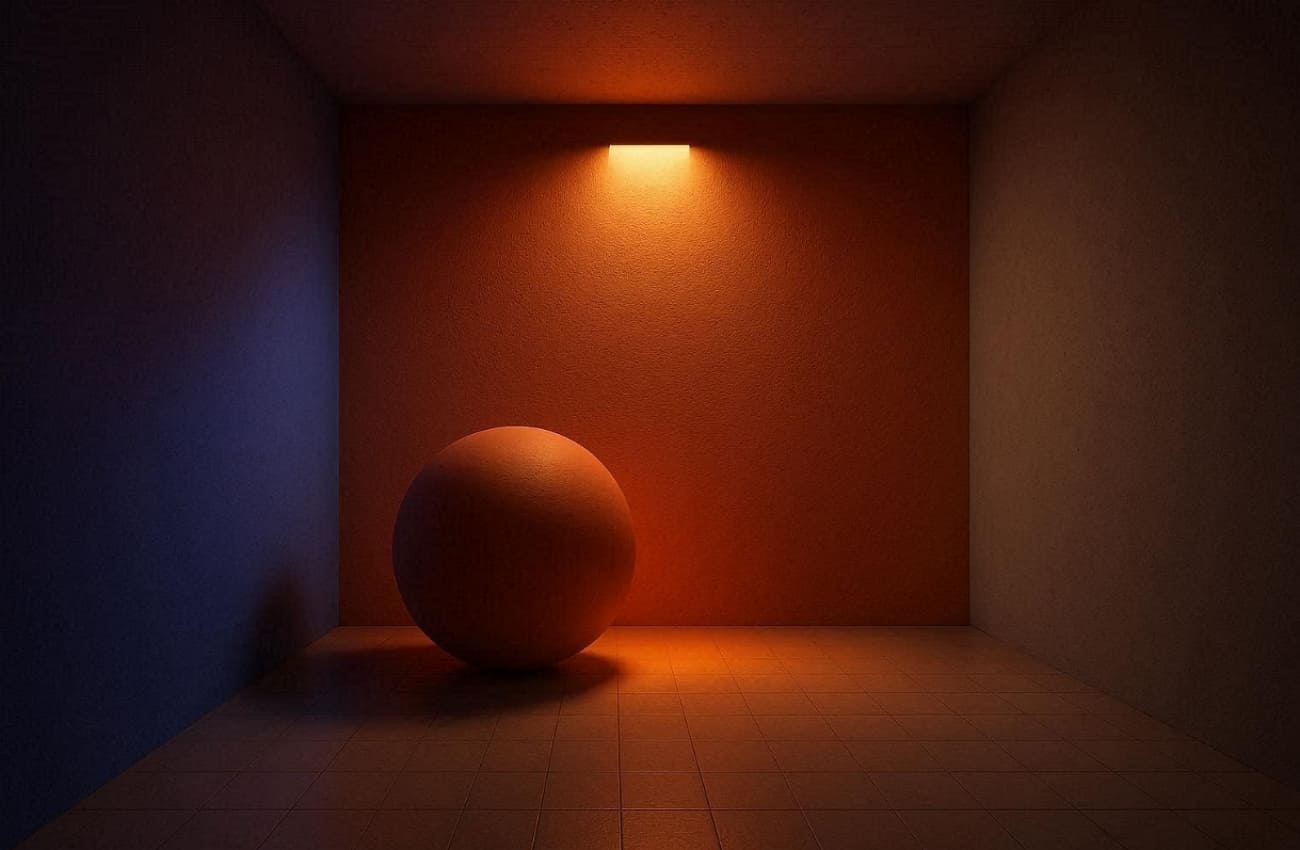

An example is one where a room has a red wall, and the light is being reflected softly, resulting in a red color on the objects near the wall. In the absence of this effect, all things are flat and artificial. The global illumination makes the scene seem more believable and balanced. With the help of GI, even minor details are more realistic, such as reflections or indirect shadows.
Part 2. What Are the Main Types of Global Illumination?
Before exploring how GI improves scenes, it helps to understand the main types of global illumination. To grasp illumination's meaning, the following are a few types to know that different techniques calculate light in unique ways:
1. Ray‑based Methods
Ray‑based methods trace light rays to mimic real lighting behavior in 3D scenes. They answer what global illumination does by showing how light bounces and spreads naturally. Techniques like path tracing and ray tracing calculate reflections and shadows.
As an example for path tracing, a Scratchapixel example shows diffuse GI with 16 samples per pixel. Thus, these methods produce realistic results but require more rendering time and computing power.
2. Photon‑based Methods
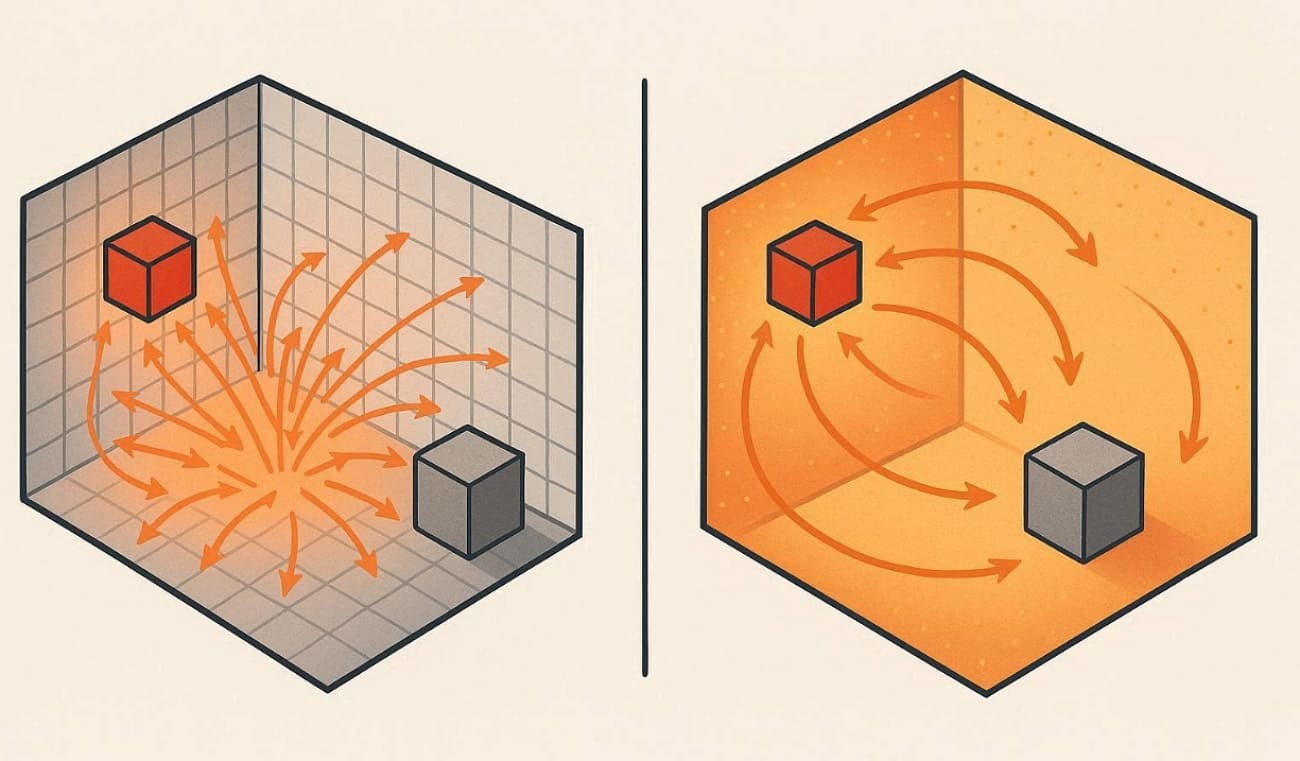
Such methods simulate how light energy travels and interacts across 3D surfaces with precision. They enhance global lighting by emitting millions of photons from light sources and storing their impacts.
During rendering, these photons reconstruct indirect illumination and bright reflections. This technique works best for scenes with complex caustics, such as glass or glossy surfaces.
3. Patch / Point‑based Methods
It divides surfaces into small elements, exchanging light energy accurately. Radiosity calculates how much light each patch sends to every other patch in scenes. According to Dassault Systèmes' rendering guide, radiosity divides surfaces into patches to solve diffuse interreflections realistically.
Point‑based GI uses surfels or point clouds to store radiance for smooth lighting. These techniques are often applied in various game engines for realistic indirect illumination.
4. Precomputed GI
Precomputed GI calculates indirect light in advance and saves it for faster real‑time rendering. This global illumination approach uses baked lightmaps or probes to capture actual lighting effects efficiently. It reduces the need for live computations, making it perfect for static or semi‑static environments.
Plus, some experts explain that lightmaps bake indirect lighting into textures during development, widely used in games for static scenes.
5. Real‑time Approximate GI
It focuses on speed, offering instant lighting reactions in dynamic 3D scenes. This answers, “what is global illumination,” by simulating bounced light quickly with limited precision. Techniques like ambient occlusion or voxel GI estimate indirect lighting using screen or voxel data. Though less accurate, they deliver believable lighting effects ideal for real‑time games.
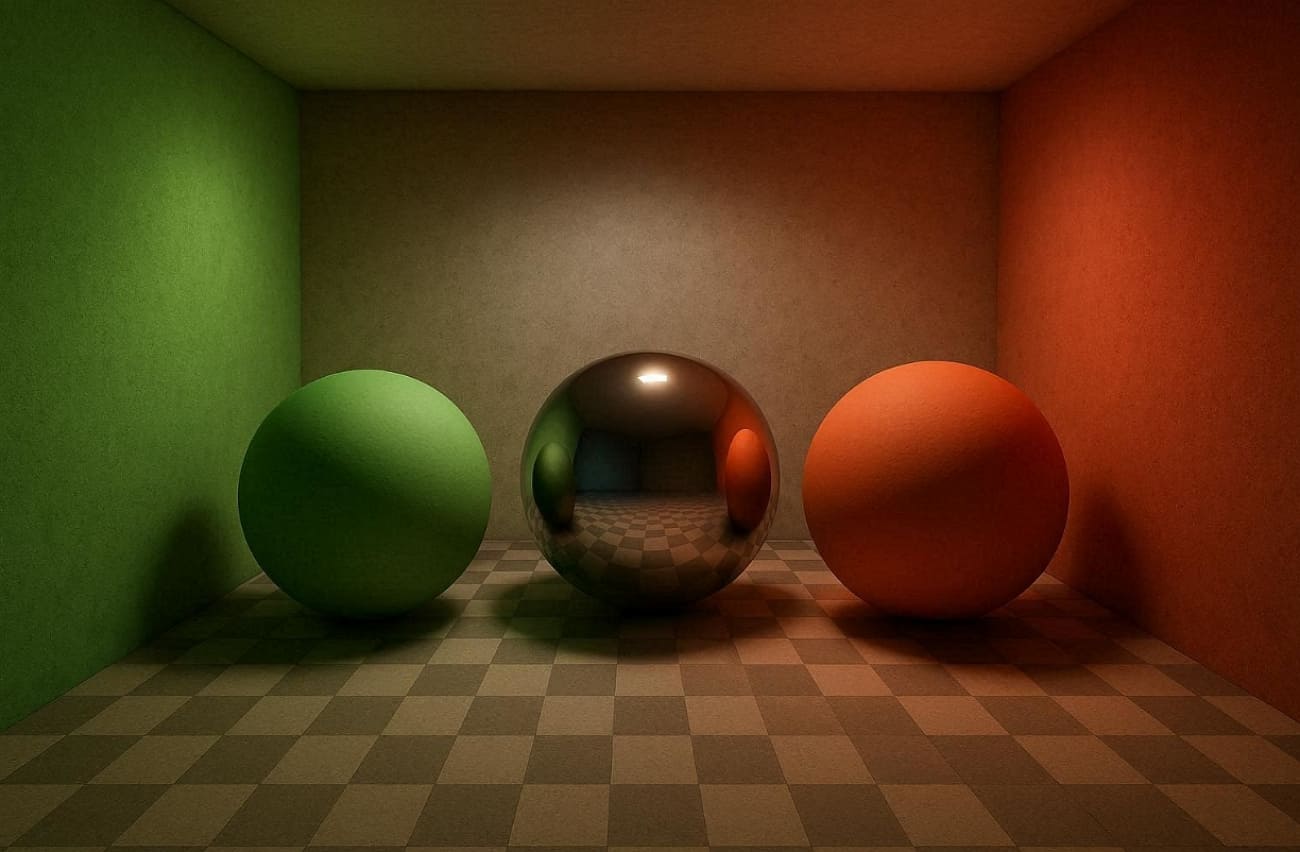

Part 3. What Does Global Illumination Do in 3D Rendering?
It improves realism by simulating how light behaves in the real world. Understanding global lighting effects helps artists create immersive visuals, with key benefits outlined below:
- Direct Light: GI calculates direct light coming straight from a light source accurately. This ensures objects facing lights are illuminated realistically without any artificial exaggeration.
- Indirect Light: GI also calculates the light that is reflected on surfaces in order to give a natural light in other regions. Even minor and dark corners are subtly lit as realistically as possible.
- Soft Shadows: Shadows are softened due to multiple bounces of light filling them partially. This prevents harsh black shadows, making scenes appear more natural and believable.
- Color Bleeding: The colors of the objects surrounding them are properly colored by the light reflecting off colored surfaces. As an example, a red wall may give a pale red shade to the surrounding objects.
- Surface Interaction: GI allows surfaces to illuminate each other through scattering and light reflection. This makes materials like walls, floors, and furniture appear interconnected naturally.
Part 4. Is Global Illumination the Same as Ray Tracing or Path Tracing?
Global illumination is not the same as ray tracing or path tracing, though they are related. So, the following table compares GI, ray tracing, and path tracing to highlight their differences clearly:
|
Aspect |
Global Illumination |
Ray Tracing |
Path Tracing |
|
Definition |
Simulates all light bounces for realistic scenes |
Traces rays for reflections, shadows, refractions |
Ray tracing with multiple random bounces |
|
Goal |
Achieve natural lighting and color bleeding |
Handle direct lighting and surface effects |
Solve full light transport accurately |
|
Indirect Light |
Always includes bounced light |
Often focuses on direct effects |
Fully simulates multi-bounce illumination |
|
Use |
Final renders, games, and architectural scenes |
Reflections, refractions, shadows |
High-end film rendering, research demos |
|
Performance |
Depends on the method chosen |
Fast for direct effects, slower for GI |
Slowest, but cleanest results |
|
Examples |
Lightmaps, photon mapping, RTGI |
Mirror reflections, glass transparency |
Pixar films, realistic interiors |
Part 5. How Do You Enable Global Illumination in Popular 3D Software?
Most modern 3D renderers include global illumination in some form, either enabled by default or configurable through settings. Each software exposes GI settings through unique panels or checkboxes. Blender uses the Cycles renderer for realistic bounces automatically.
Maya enables GI through Render Settings with Arnold integration. 3ds Max activates Mental Ray or V-Ray GI options. Unreal Engine offers Lumen for real-time GI effects. Below are detailed steps for enabling GI in Unreal Engine specifically:
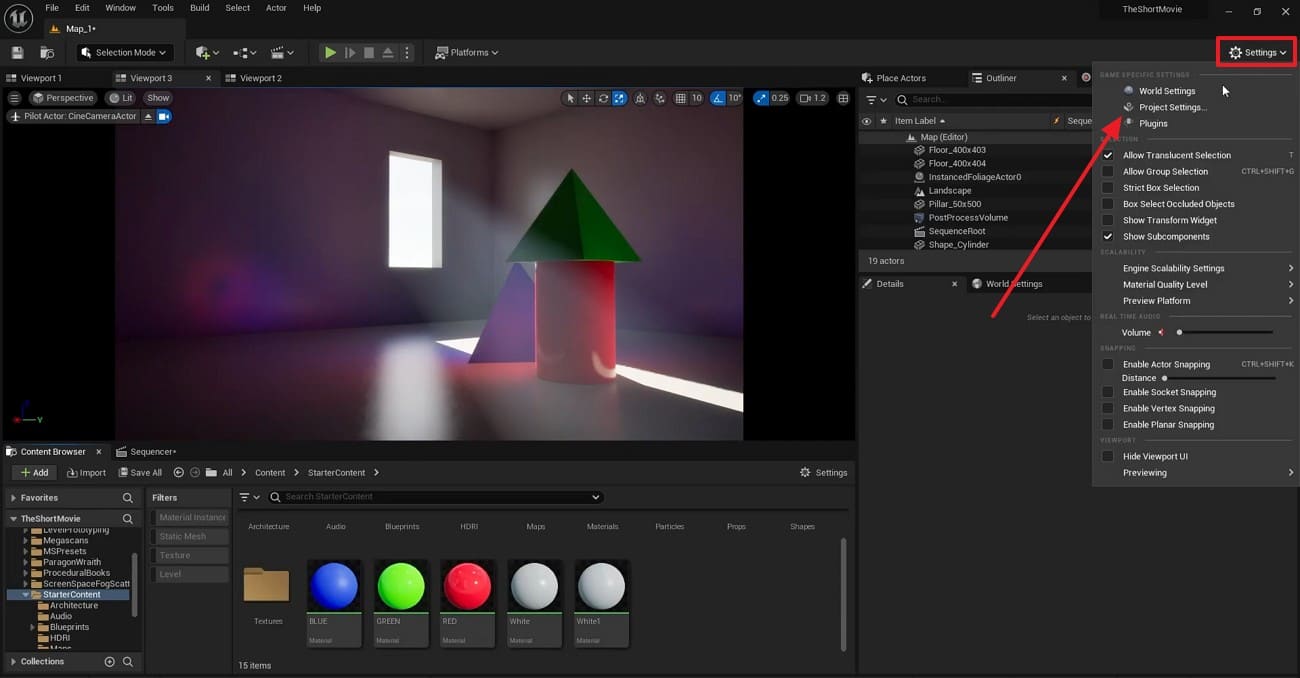
Step 1. Upon accessing the working panel, click the “Settings” option and head to “Project Settings. ”
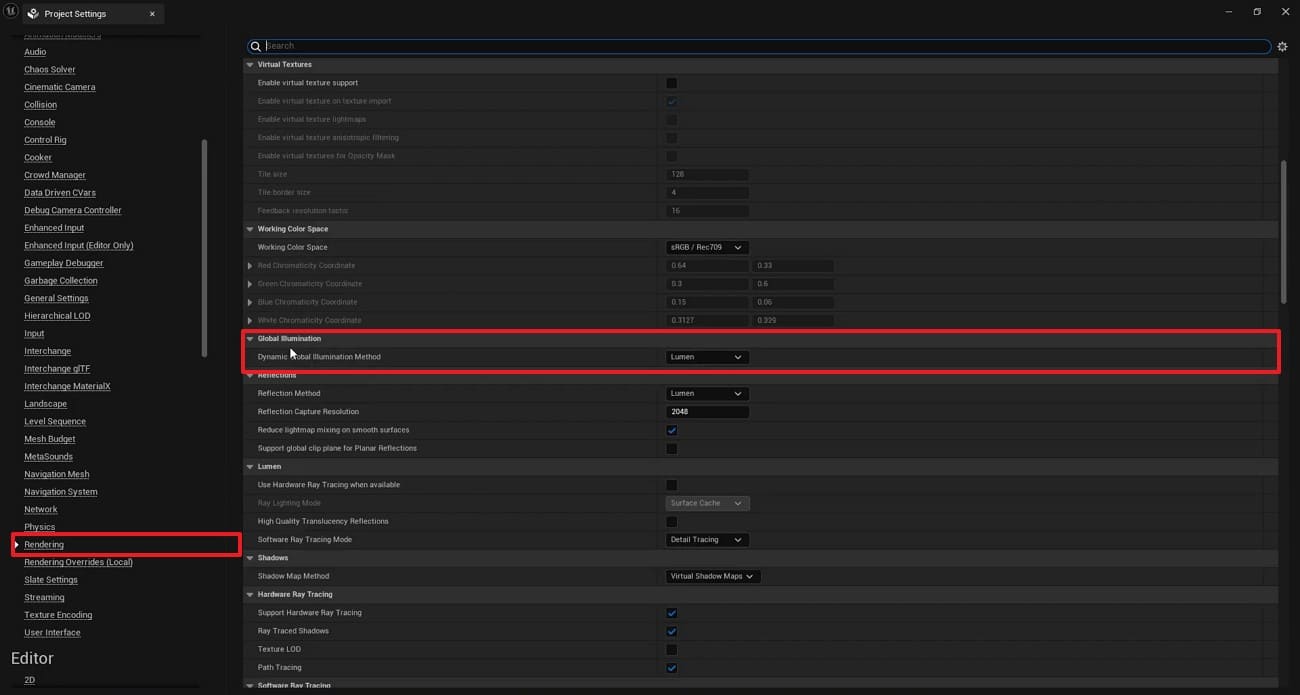
Step 2. Go to the “Rendering” tab under the “Engine” section. Afterward, make sure the “Global Illumination” is set to “Lumen.”
Part 6. How Can You Speed Up Global Illumination Rendering?
Rendering global lighting takes much time due to complex light calculations. Simple tricks help finish renders faster while keeping quality high. Thus, the tips below show practical ways to save time effectively:
1. Reduce Bounces and Samples
Lower maximum light bounces from 32 to 8 for faster rendering times. Moreover, use fewer samples per pixel for draft renders instead of final shots. Path tracers show significant speed gains with minimal visual quality loss. Blender tests confirm that reducing diffuse bounces from full GI cuts renders time effectively.
2. Use Smarter Termination and Caching
Enabling smarter termination, like Russian roulette, reduces low-energy rays, saving rendering time effectively. What global illumination does is computed efficiently with less ray tracing work. GI caches, such as the irradiance cache, significantly speed up rendering. Low-accuracy cache settings in Redshift render fastest for drafts. These techniques balance speed and realistic lighting quality well.
3. Mix Baked and Dynamic GI
Bake lightmaps for static objects to save real-time computation power. Use GI game engines like Unreal Engine's GPU Lightmass for static geometry only. In addition to this, reserve dynamic GI for moving characters or key objects. This hybrid approach dramatically speeds up complex scene rendering significantly.
4. Use Cloud Rendering for Complex Projects
For heavy GI scenes, a single workstation is hard to handle well. In these cases, many artists choose to use a render farm to handle long or complex GI renders. Fox Renderfarm, a professional cloud rendering service, offers thousands of GPU nodes for simultaneous frame rendering.
Fox Renderfarm has high-speed transfers and SSD storage that removes I/O bottlenecks. This cloud rendering service is also compatible with famous 3D software, including 3ds Max and Maya. It turns multi-day projects into hours with cost-effective GPU pricing.

5. Optimize Geometry and Ray Traversal
Use BVH acceleration structures to speed up global lighting ray calculations significantly. Clean scenes by removing tiny unseen high-poly details to reduce intersection tests. Besides, path tracer optimizations effectively reduce ray-triangle tests by 70%. Moreover, improved BVH structures reduce render time from 1,800 seconds to 94 seconds. This delivers nearly 19 times faster rendering with combined optimizations.
Part 7. Is Global Illumination Expensive? When to Use?
Global illumination can be costly because it calculates many light bounces instead of just direct light. The table below shows when its extra rendering cost is justified and when you can skip it:
|
When GI Is Worth It |
When GI Can Be Skipped |
|
Film-level realism shots |
Simple real-time previews |
|
High-end archviz interiors |
Fast gameplay prototyping |
|
Product hero renders |
Stylized flat-lit scenes |
|
Atmospheric cinematic scenes |
Mobile or low-spec targets |
|
Physically based lighting setups |
Non-photoreal quick drafts |
Part 8. FAQ about Global Illumination
Q1. Do I really need global illumination for realistic rendering?
It is not necessary to have global illumination, but it is essential for realistic lighting. This introduces bounced light and color bleeding, which are difficult to obtain with direct lights. For interiors and film scenes, using GI is strongly recommended.
Q2. Why does global illumination make rendering so slow?
Global illumination simulates multiple light bounces between surfaces, which significantly increases the number of rays that need to be computed. This puts heavy pressure on both CPU and GPU resources. To handle heavy GI efficiently, artists often rely on render farm such as Fox Renderfarm.
Q3. What is the difference between baked GI and real-time GI?
Baked GI pre-computes lighting into lightmaps before runtime for fast performance. Real-time GI calculates bounced light dynamically during scene rendering continuously. So, baked works best for static scenes, while real-time handles moving objects flexibly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, global illumination brings 3D scenes to life with natural light bounces and soft shadows. This guide explains what global illumination does and how to use it more efficiently. While GI greatly improves visual quality, it also increases rendering cost and computation time.
For heavy rendering tasks that take days locally, we recommend to use a render farm like Fox Renderfarm to process complex GI renders more efficiently.





